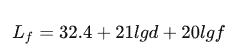The propagation of electromagnetic waves is related to frequency. There are ground waves, sky waves, space waves and scattered waves in the propagation modes. Sky waves and space waves are used daily. Generally speaking, the frequency of radio waves used to transmit signals is between 3MHz and 10GHz. 3-30M is short wave, relying on ionospheric radiation, can achieve global communication, so the coverage is global, but depends on environmental factors.
30-300M is very high frequency VHF, which usually uses FM to transmit broadcast signals, that is, FM radio stations such as traffic broadcasts in various regions. Because it can achieve better transmission effects, it is the main force of local radio stations. Different from short wave, VHF It is mainly line-of-sight propagation, that is, you can see as many places as you can, and basically cannot be transmitted back through the atmosphere. Of course, mountains and other things will also cause signal attenuation. Generally speaking, the coverage radius is about tens of tens of meters. km, but some stations will use multiple sets of antennas to transmit, so the coverage will be larger.
300M-3GHz is UHF, and the transmission form is similar to VHF, but it is not open to local radio stations for transmission. It is generally used for walkie-talkies, handheld and car radios.
All of the above have a lot to do with the antenna. If you transmit directionally, the 144Mhz frequency band can even achieve the ground-moon-ground propagation path. Since the broadcast is non-directional, it mainly depends on your distance from the transmission tower, just like a mobile phone. The signal is the same, too far away.
There are too many factors in the calculation of the above reference, so I simply copy a cheat sheet. When the propagation path of the radio wave is far from the ground and the influence of the atmosphere on the propagation of the radio wave can be ignored, the free space propagation model is adopted, which is not applicable under other complex conditions, for reference only:
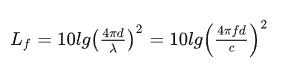 The definition and formula refer to ITU Rec.P.525, where L is the loss (dB), d is the propagation radius (km), and f is the frequency (MHz). The engineering formula can be simplified as:
The definition and formula refer to ITU Rec.P.525, where L is the loss (dB), d is the propagation radius (km), and f is the frequency (MHz). The engineering formula can be simplified as: