Analog TV Transmitter Analysis
In-depth analysis of the principle of TV transmitter and the characteristics of analog TV transmitter
A TV transmitter is a device that takes a video and audio signal and transmits it to an antenna to be broadcast as television. The principles behind TV transmitters are based on amplitude modulation (AM) and frequency modulation (FM) techniques.
Analog TV transmitters work by modulating the amplitude and frequency of a carrier wave to transmit the video and audio signals. The video signal modulates the amplitude of the carrier wave, while the audio signal modulates the frequency of the carrier wave.
The characteristics of analog TV transmitters are:
- Bandwidth: Analog TV transmitters have a relatively large bandwidth compared to digital TV transmitters. This is because the analog signal is continuous and has a wide range of frequencies, whereas digital signals are made up of binary data and have a smaller bandwidth.
- Interference: Analog TV transmitters are more susceptible to interference from other signals and sources of noise, such as electrical equipment and other electronic devices.
- Picture and Sound Quality: Analog TV transmitters have a limited picture and sound quality compared to digital TV transmitters. The quality of the analog signal can degrade with distance, and the picture can become fuzzy and the sound distorted.
- Coverage: Analog TV transmitters have a limited coverage area compared to digital TV transmitters. This is because the signal strength decreases with distance and can become weak or even disappear completely beyond a certain range.
- Channel Capacity: Analog TV transmitters have limited channel capacity, meaning that only a limited number of channels can be transmitted at one time. In contrast, digital TV transmitters have a much larger channel capacity.
Overall, analog TV transmitters have been replaced by digital TV transmitters in most countries due to the superior picture and sound quality, increased channel capacity, and improved coverage offered by digital TV. However, analog TV transmitters may still be in use in some areas where digital infrastructure is not yet available.
Both the image signal and the audio signal are transmitted at the same time.
Transmit in VHF (meter wave) and UHF (decimeter wave) bands.
Image transmission adopts amplitude modulation and vestigial sideband mode.
The audio transmission adopts frequency modulation.
Using intermediate frequency modulation;
Image intermediate frequency: 38MHz, audio intermediate frequency; 31.5MHz (PAL-D/K system)
The frequency difference between the image carrier frequency and the sound carrier frequency must be kept strictly constant.
The image to sound power ratio is usually 10:1
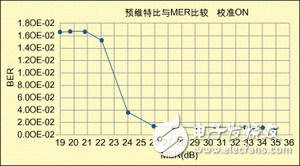
The intermediate frequency pre-correction technology ensures superior cost performance.
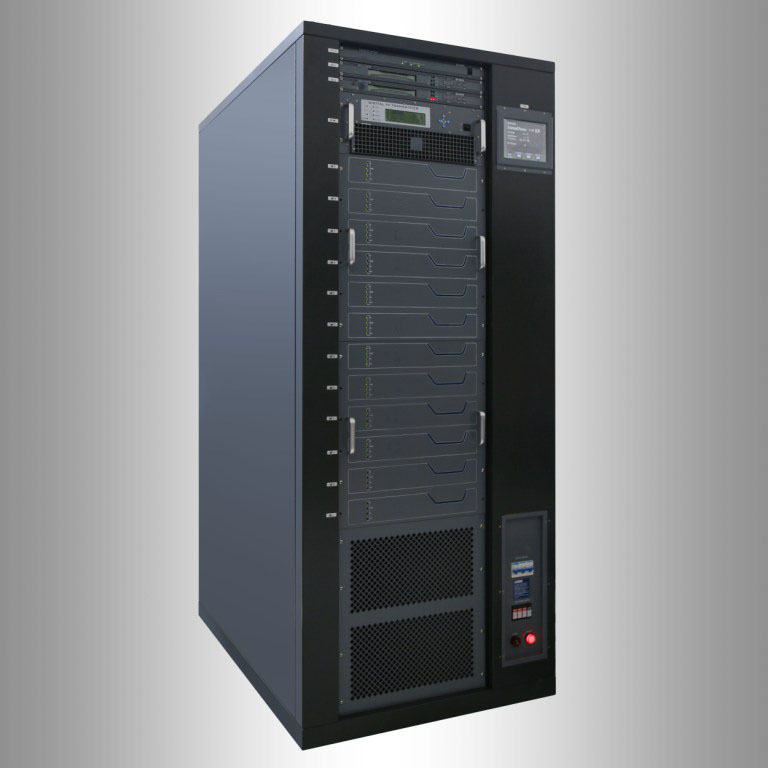
TV transmitter single-channel transmitter and dual-channel transmitter.
Contemporary TV transmitters adopt an all-solid-state single-channel method.
The all-solid-state power amplifier adopts cascaded power amplifiers, the power gain is greater than 40dB, and the final power amplifier works in Class AB.
Intelligent monitoring system, simple operation and convenient maintenance